Large Combustion Plants (LCP)
5.2- Large Combustion Plants (LCP)

This indicator is an important pressure indicator that affects air pollution. Large combustion plants consume large amounts of fuels, mostly fossil fuels, to produce useful energy, as they are plants with a nominal thermal power of 50 MW or more. Emissions from large combustion plants account for a large portion of total man- made pollutant and greenhouse gas emissions. The goal of related legislation is to reduce emissions of acidifying pollutants, particulate matter, and ozone precursors. More effective pollution reduction requires a systematic transition to low-carbon and cleaner alternatives in energy generation. [35].
The total thermal capacity of the Large Combustion Plants in Turkey was 82 GWth in 2016 and it increased by percent 42 to 125 GWth in 2017[36].
Total installed capacity in EU-28 countries was 1287 GWth in 2017. There has been a decrease in the total fuel consumption in combustion plants as a result of European Union policies on air quality, public health, and climate change. More effective measures are expected to be taken under the New Green Consensus to achieve zero pollution and decarbonization targets, and to replace fossil fuels with renewable resources.[37].
GRAPH 25- NUMBER OF LARGE COMBUSTION PLANTS
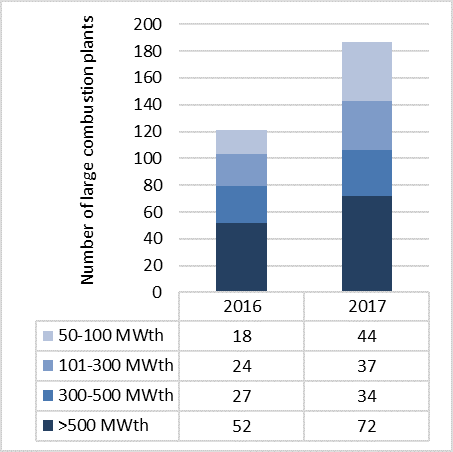
Source: Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change, General Directorate of Environmental Mana- gement, 2020
GRAPH 26- LARGE COMBUSTION PLANTS TOTAL THERMAL POWER
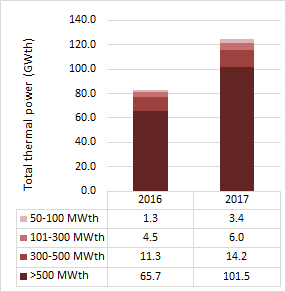
Source: Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change, General Directorate of Environmental Mana- gement, 2020



